Comparison
A Comparison widget displays a summary table with the values of the selected data attributes in different groups.
Use the widget to compare multiple values from different categories within a single widget. For example, you can compare the average bill in restaurants from different areas of the city.
Case example: compare the average number of floors in buildings from different administrative districts:
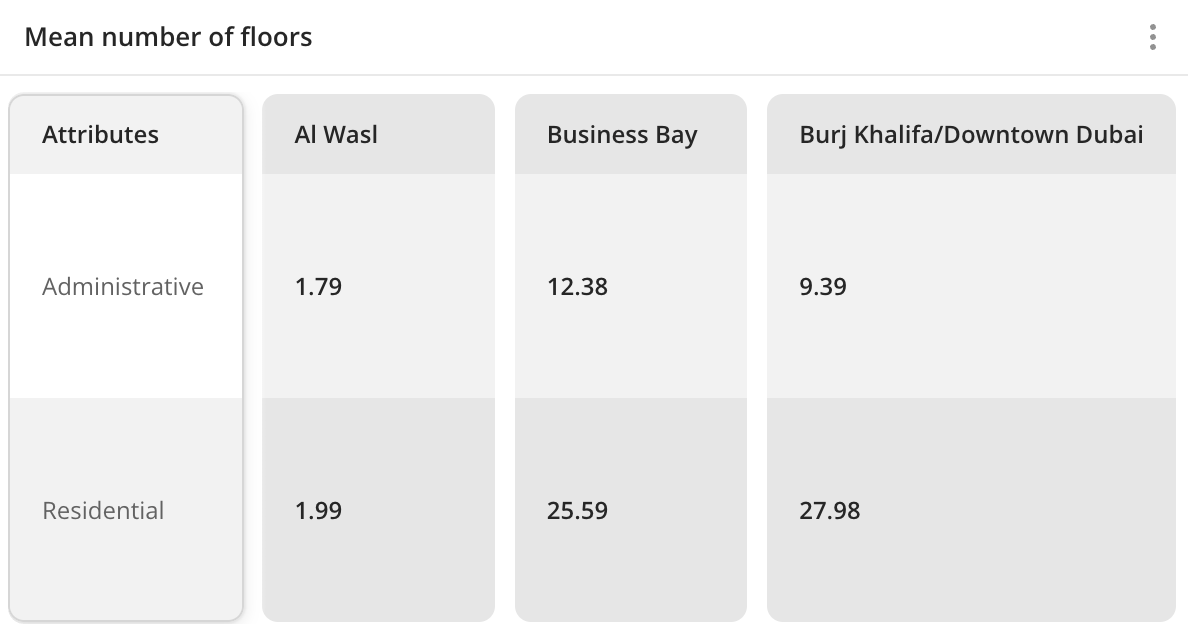
Main features
-
The values of comparison attributes are grouped in the widget by columns. As groups, you can select:
-
Territories:
- Standard territories: regions, districts, settlements, and others.
- Custom territories: first upload your own dataset with polygons and create a territory filter.
- Territories specified in geofilters for the current dashboard scene.
For more information on territory types, see the Geofilters section.
-
Data visualization elements in layers: H3, Contour, or Polygon. You can select elements by clicking them on the map. Example:
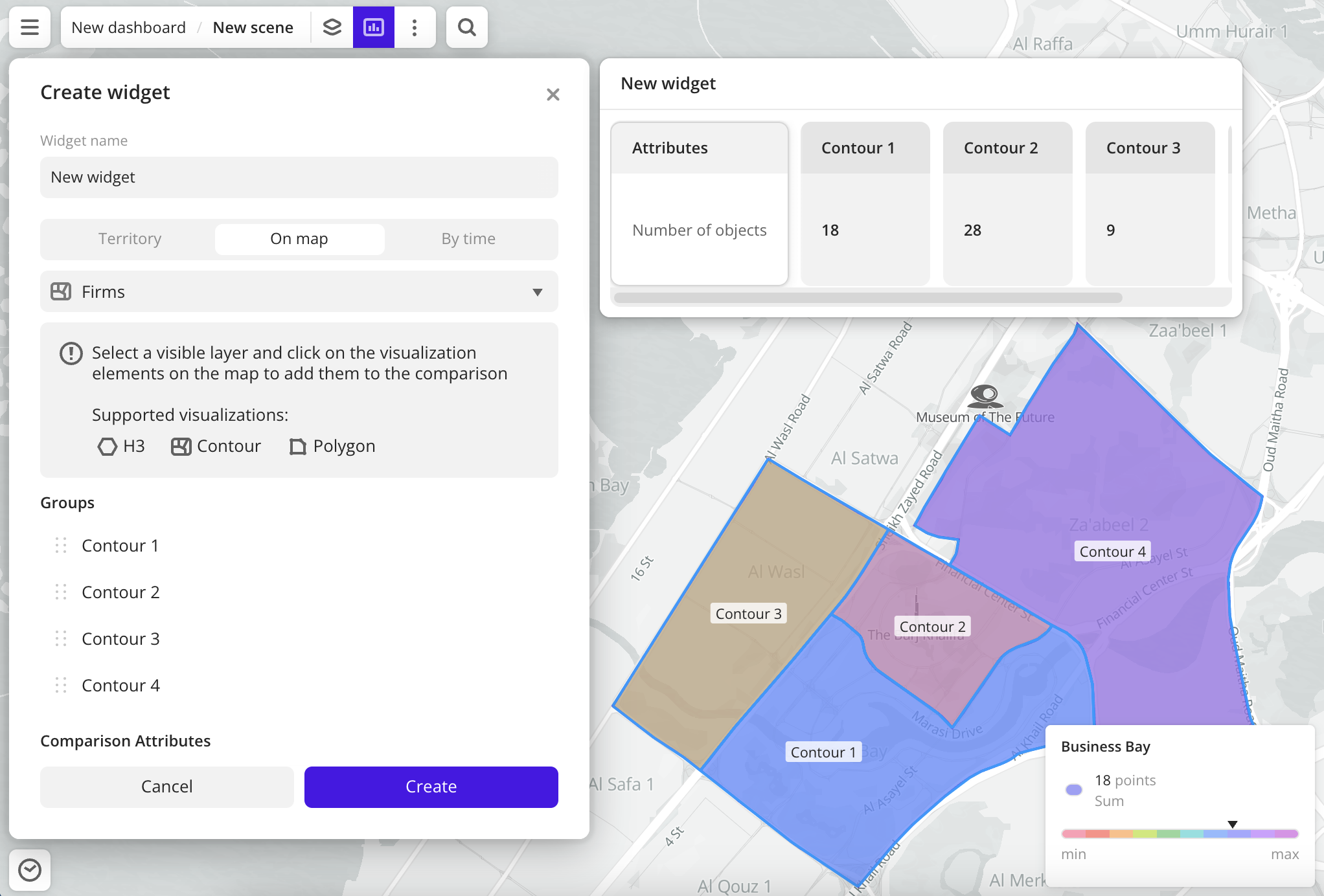
-
Time ranges.
-
-
Each column contains the values of the selected comparison attributes (aggregation attributes). The attributes can belong to different data layers. As comparison attributes, you can select:
- Numeric attributes: to count the number of values in the sample or to count values of the attributes using aggregation functions: total, mean, minimum, maximum value, median, and percentile.
- Text attributes, logical attributes, or number of objects: to count the number of values in the sample.
-
The maximum number of groups (columns) in the widget is 100. The maximum number of comparison attributes is 100.
-
If necessary, you can edit the names of the comparison attributes displayed in the widget. The attribute names in the dataset will not change.
-
Changes in layer data are automatically reflected in the widget.
-
If the filtering by territories or data attributes is applied on a dashboard scene, only the values that match the filters are displayed in the widget. For more information, see the Filtering data on a dashboard instruction.
Creating a widget
-
Go to the Dashboards tab.
-
Open the required dashboard.
-
Open the scene using the arrows
and
. If the dashboard has only one scene, it will open automatically.
-
In the top menu of the dashboard, click the
icon.
-
Select the Comparison widget type.
-
Specify the required parameters:
- Groups: territories, visualization elements, or time ranges for which attribute values are calculated.
- Comparison attributes: values displayed in the widget:
- Layer: data layer containing the required attributes.
- Aggregation attribute: attribute used to aggregate data and calculate the values.
- Aggregation type: function used to calculate aggregation attribute values.
-
Set the remaining widget parameters if necessary.
-
Click Create.
The new widget is automatically added to the selected dashboard scene.
Note
When working with the uploaded data, make sure it contains at least one attribute to display a value in the widget.
Parameters
General widget settings
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Widget name | Widget name. |
Groups
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Territory | Selecting territories as groups for comparison. You can select:
|
| On the map | Selecting data visualization elements (H3, Contour, or Polygon) as groups for comparison. Select a layer with data visualization (the layer must be shown on the scene) and click the required elements on the map. |
| By time | Selecting time ranges as groups for comparison. Available only for layers from datasets containing attributes with the Date type.As values, you can select the following:
|
| Groups | To change the order of groups (columns) in the widget, hold The feature is not available if you use the Synchronously with geofilters option or if you select the By time grouping. |
Comparison attributes
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Layer | Data layer containing the required comparison attributes:
To add another data layer, click Add layer. The feature is not available if you use the On the map grouping. To change the order of layers and the corresponding attributes in the widget, hold The maximum number of layers is 100. |
| Aggregation attribute | Attribute, which value is aggregated and displayed in the widget:
When the data value changes, the value in the widget is also updated automatically. To add another data attribute, click Add attribute. To change the order of attributes (rows) of one layer in the widget, hold The maximum number of attributes for each layer is 100. |
| Aggregation type | Function used to calculate values of the comparison attribute (aggregation attribute) in each group. For numeric attributes:
For text attributes, logical attributes, and number of objects:
|
| Formatting | Format of the comparison attribute (aggregation attribute) value displayed in the widget. To change the format, click
|
| Attribute name | To rename a comparison attribute (aggregation attribute) displayed in the widget, click |
What's next?
- Get to know more about other Widgets types.
- See available Operations with widgets.
- Quick start.
- Get to know how to work with Data and Data visualization.
- Get to know more about Layers, Dashboards, and Scenes.
- Get to know Analytics scenarios.